Getting Started With Docker - Quick Start Guide
Getting Started With Docker - Quick Start Guide
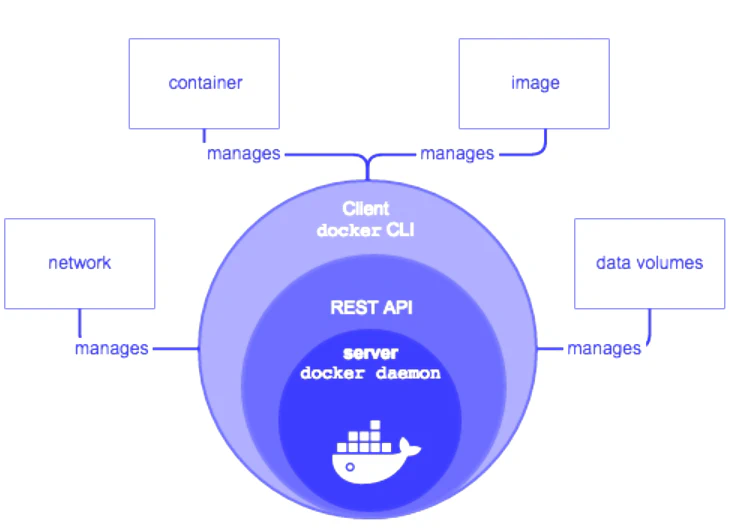
Docker Engine
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Cloud platform service. Allows you to manage its application and data. Cloud service provider manages servers, storage, networking, and computing power.
- Provides OS level virtualization platform
- The OS kernel allows multiple isolated instances.
Components of the Docker Engine
- Docker Daemon:
- Brain of the Docker
- Persistent background process ( such as our normal system service, which runs continuously.)
- Process named “dockerd” listens for Docker API requests and manages Docker objects. (create docker images, run docker containers, route traffic among Docker containers.
- Manages Docker Objects.
- Docker images
- Docker Containers
- Docker Networking
- Docker Volumes
- Docker Engine REST API:
- Docker API used to keep interaction with Docker Daemon.
- Communication performed using HTTP requests.
- Application Programming Interface (API)
- This API communicate using UNIX Socket (unix:///var/run/docker.sock)
- Docker CLI
- Command Line Interface.
- This user interface allows the user to manage Docker objects and communicate to Docker daemon.
Docker Engine - Birds Eye View
Docker Architecture
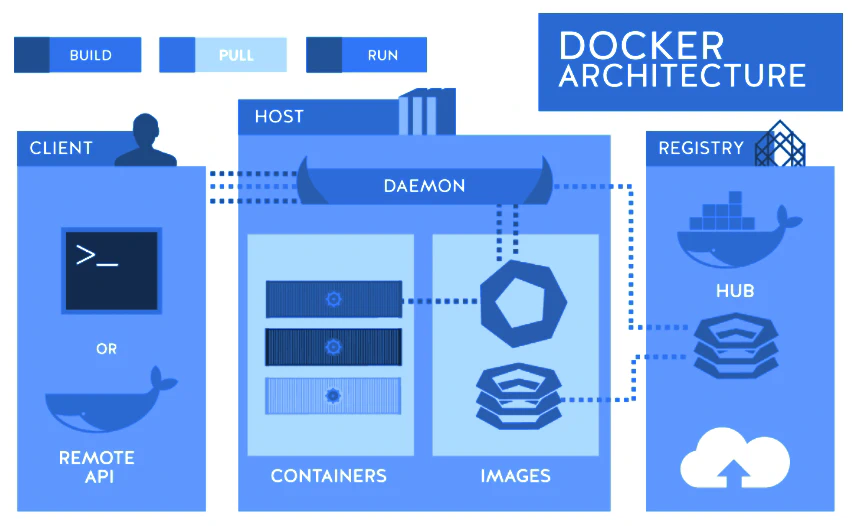
- Docker architecture consist of 3 main components
- Docker Client
- Docker Host
- Docker Registry
- Docker Client - This is where we are doing stuff
- Enables us to interact with Docker daemon
- Docker Clients typically reside on the same host where Docker daemon is running. But in some cases, it can run on a remote host as well.
- Docker client provides us to command line interface to issue command to Docker daemon (docker build, docker run.. )
- Docker Host
- Provides a complete infrastructure to execute and run applications
- Main control center
- Docker daemon pulls images from docker registry and build container images and run application as we requested by Docker CLI/ Docker Client
- Docker Objects
There are numerous objects available. One or more objects required to run an application in a container.
- Images
- Containers
- Networking
- Storage
3.1. Docker Images
- Each of the files in a Docker image consist it’s own layer.
- Use to build containers
- Use to store and ship containers
- Read only binaries snapshot or template
- Consist of File system and required libraries to run a specific application environment
- Shareable using public / private registry
- Consists a series of layers and each command composed to a read-only layer.
3.2. Docker Containers
- Encapsulated environments which can run applications
- Running instance of a Docker image
3.3. Docker Networking
- Bridge network
- Overlay network
- Macvlan network
- Null
3.4. Docker Storage
- Data Volume
- Support persistent data storage. (data will not loss even after the container restart/delete)
- Data volumes resides on the host file system
- Container data can accessible from host-file system
- Scenarios - Running state full applications
- Data Volume Container
- This volume type can share among multiple containers
- This is independent from application container - shared volumes
- Scenarios - sharing same configuration among multiple containers
- Directory Mount
- Directly mount the host’s local directory into a container.
- Any directory on the host can be mounted as a source for the container volumes.
- Scenarios - mounting hosts .ssh folder, .bash_profile file, .kubectl folder into container to share the same host configuration to the container.
- Storage Plugins
- Allows to connect other storage types such as data LUNs, SAN storages, NFS, SAMBA
- There are number of storage plugins available
- Azure File Storage, EMC
- Docker Registry
- This is where docker images can store
- There may be private and public registries
Creating a Dockerfile
| Command | Usage |
| FROM | To specify the parent image. |
| WORKDIR | To set the working directory to execute the command within the directory |
| RUN | To install packages that are need to run specific application |
| COPY | To copy over files or directories from a source to destination |
| ADD | Same as COPY command. But, also able to handle remote URLs and unpack compressed files. |
| ENTRYPOINT | Command that will always be executed when the container starts. If not specified, the default is /bin/sh -c |
| CMD | Arguments passed to the entrypoint. If ENTRYPOINT is not set (defaults to /bin/sh -c), the CMD will be the commands the container executes. |
| EXPOSE | To define which port through which to access your container application. |
Sample Dockerfile
#Download base image ubuntu 20.04
FROM ubuntu:latest
USER root
# labels about the custom image
LABEL maintainer="NGINX Sample WebServer"
LABEL maintainer="dimuit86@gmail.com"
LABEL description="This is custom Docker Image for \
DigitalAvenue DevOps."
# Update the image to the latest packages \
# Install Nginx
RUN apt-get update -y && \
apt-get install nginx -y && \
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && \
apt clean
RUN rm -rf /var/www/html/*.html
COPY ./index.html /var/www/html/index.html
# Volume configuration
VOLUME ["/var/log/nginx", "/var/www/html"]
# Expose Port for the Application
EXPOSE 80 443
# Last is the actual command to start up NGINX within our Container
CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]
Dockerfile Definitions
- FROM : parent image/ base image use to create a container with a specific application
- LABEL : Define a description, ownership, authority
- RUN : Specific command to make changes to base image.
- Install new applications, packages, libraries
- Adding new users
- Changing file permissions and ownership
- USER : Defines the username that all the commands will be run as the mentioned user.
- WORKDIR : Defines default working directory where all the commands are going to be executed. WORKDIR comes before “ENTRYPOINT” OR “CMD”
- CMD : This command runs when the container starts
- ENTRYPOINT : This is where the default application is going to start when the container is created.
Practical 01: Containerize NGINX Web Application
In this demonstration, we are going to spin up a simple Nginx website using Docker Ubuntu base image. And we’ll copy custom “nginx.conf” configuration files and “index.html” files into the docker container.
STEP 01: Create a “index.html”
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Hello, Nginx!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, Digital Avenue!</h1>
<p>We have just configured our Nginx web server on Ubuntu Server!</p>
</body>
</html>
STEP 02: Create Custom “nginx.conf” file
user www-data;
worker_processes auto;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
include /etc/nginx/modules-enabled/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 768;
}
http {
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3; # Dropping SSLv3, ref: POODLE
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
gzip on;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
}
STEP 03: Create a Dockerfile
#Download base image ubuntu 20.04
FROM ubuntu:latest
# labels about the custom image
LABEL maintainer="NGINX Sample WebServer"
LABEL maintainer="dimuit86@gmail.com"
LABEL description="This is custom Docker Image for \
DigitalAvenue DevOps."
# Update the image to the latest packages \
# Install Nginx
RUN apt-get update -y && \
apt-get install nginx -y && \
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && \
apt clean
RUN rm -rf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
RUN rm -rf /var/www/html/*.html
COPY ./nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
COPY ./index.html /var/www/html/index.html
# Volume configuration
VOLUME ["/var/log/nginx", "/var/www/html"]
# Expose Port for the Application
EXPOSE 80 443
# Last is the actual command to start up NGINX within our Container
CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]
docker build -t nginx-web:v1 .
docker run -d -p 8080:80 –name nginx-web nginx-web:v1
http://localhost:8080
Build a Docker Image:
docker build -t
Run Docker Container
docker run -d -p 8080:80 –name
Inspect Docker Container
docker container ls
docker container <CONTAINER-NAME/ID>
Log into Docker Container
docker run -it <CONTAINER-NAME/ID>
Accessing Docker Volumes:
Docker Volume Location:
Linux : /var/lib/docker/volumes/
Windows WSL: Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL2)
Ctrl + R = “\wsl$\docker-desktop-data\version-pack-data\community\docker\volumes”
Practical 02: Containerized Node Application - Multi Stage Docker Images
# ================================================================
# B U I L D E R S T A G E
# ================================================================
FROM node:14-alpine AS builder
LABEL Name="Node.js Demo App - MULTI STAGE"
LABEL maintainer="dimuit86@gmail.com"
LABEL description="This is custom Docker Image for \
DigitalAvenue DevOps."
ENV NODE_ENV production
# Create app directory
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
WORKDIR /app
# Copy package.json and .lock file
# from host to docker container
COPY package.json package-lock.json ./
# Installing dependencies
# RUN npm install
# For Production usage
RUN npm ci --only=production
# Bundle app source
COPY . .
# ================================================================
# D E P L O Y S T A G E
# ================================================================
FROM nginx:1.19-alpine AS server
# Copy custom nginx.con file
COPY ./nginx.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
# Copy build output from build stage
COPY --from=builder /usr/src/app /usr/share/nginx/html
# Open port 80
EXPOSE 80
# Start nginx from backgrood
CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]
docker build -t nodejs-web:v1 .
Deploy Production Grade Kubernetes Cluster on Azure AKS
Introduction This tutorial is intended to demonstrate how to setup your 1st Kubernetes cluster on Azure Kubernetes Services (AKS). This tutorial will cover up all the steps that you need to setup complete AKS cluster.
How To Run Microsoft SQL Server On Kubernetes - Azure Kubernetes Service
Prerequisites: Azure CLI https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli 1. Run the Azure CLI with the az command. 1.1 Run the login command. az login Login in the browser with the azure account.
How To Setup Jenkins Server on Kubernetes - Master Slave Setup
Jenkins is the most commonly used and popular open-source CI/CD tool used by many famous companies worldwide. We don’t need to have a second thought of it since the biggest companies like Facebook, Udemy, NetFlix, LinkedIn and many more companies using Jenkins with confidence.


